Why characterize extractables and leachables?
Extractables are defined as compounds that can be extracted from packaging materials or devices under controlled experimental conditions. Leachables, a subset of extractables, are compounds that actually migrate into the final product during the expected shelf life or contact time.
The characterization of extractables and leachables has become increasingly important due to growing global regulations. Because of their potential impact on patient health, many professional sectors are confronted with the problem of extractables and leachables, including the biopharmaceutical sector.
The implementation of extractable and leachable substance tests from the design stage through to the marketing of containers is therefore an essential prerequisite. These tests demonstrate that the concentration of contaminants does not exceed acceptable or regulatory thresholds.
The extractables and leachables that can potentially migrate to the contents obviously depend on the raw materials and manufacturing processes involved in the design of each container, and may be organic or inorganic species.
The diversity of extractables and leachables that can be investigated implies the use of high-performance analytical equipment to perform the various relevant analyses.
The guidelines available for extractables and leachables are specific to each manufacturer’s sector of activity, but include ICH Q3D, USP 233 (US Pharmacopoeia no. 233: Elemental Impurities – Procedures) and BPOG.
USP 233 and ICH Q3D are guidelines for the analysis of elemental impurities in pharmaceutical products.
USP 233 describes specific, quantitative analytical procedures for each elemental (inorganic) impurity in pharmaceutical products and ingredients. The USP chapter recommends the use of instrumental techniques such as inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) or ICP-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). USP also recommends the use of closed containers for digestion of solid samples to ensure quantitative recovery of all regulated analytes, including volatile elements such as mercury.
ICH Q3D establishes the methodology for the assessment of elemental impurities in pharmaceutical products, including medicinal products for human use. In particular, ICH Q3D recommends an assessment of the risk associated with the presence of elemental impurities in health products. This can be done by means of qualitative or quantitative screening.
The BPOG standard is a set of best practices for the production of biopharmaceutical drugs. It was developed by the Biophorum Operations Group (BPOG), an international organization of biopharmaceutical industry experts. The BPOG guidelines provide recommendations for the manufacture of biopharmaceutical products, including monoclonal antibodies, vaccines and gene therapies.
Why choose TERA Environnement to characterize your extractables and leachables?
- Find out why you should choose our laboratory to help you characterize extractables and leachables:
- High-performance analytical equipment for your analyses
- Wide range of compounds that can be analyzed
- Very low analytical thresholds or limits of quantification (LOQ) ranging from ppt to ppb, enabling compliance with regulations
- Flexibility and responsiveness
- Customized study of your specifications to offer you all the analyses you need to study your extractables and leachables
- Experience in managing project to various standards: BPOG, USP 233 and ICH Q3D etc.
What technical resources do we have to characterize extractables and leachables?
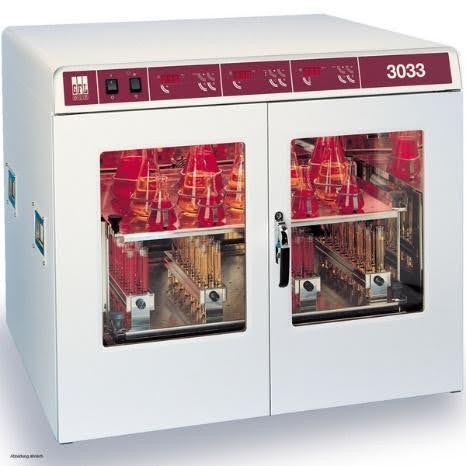

- Enclosures for prolonged extraction of your containers before analysis of extractables or leachables
TERA Environnement has a range of enclosures, with or without agitation, and with temperature control up to 100°C.
Containers can be extracted with various organic or inorganic solvents, medicinal solutions, etc.
- Preparation of extracts before analysis of extractables or leachables
Pre-concentration steps such as liquid extractions, acidifications and dilutions, as well as microwave mineralization techniques, may be required before extractables analysis.
- High-performance analytical equipment
TERA Environnement has a range of analytical equipment to help you find inorganic and organic extractables and leachables.
- Aluminium (Al); Antimony (Sb); Silver (Ag); Arsenic (As); Barium (Ba); Bismuth (Bi); Boron (B); Cadmium (Cd); Calcium (Ca); Chromium (Cr); Cobalt (Co); Copper (Cu); Tin (Sn); Iron (Fe); Germanium (Ge); Iridium (Ir); Lithium (Li); Magnesium (Mg); Manganese (Mn); Mercury (Hg); Molybdenum (Mo); Nickel (Ni); Gold (Au); Osmium (Os); Palladium (Pd); Platinum (Pt); Lead (Pb); Potassium (K); Rhodium (Rh); Ruthenium (Ru); Selenium (Se); Silicon (Si); Sodium (Na); Strontium (Sr); Thallium (Tl); Titanium (Ti); Tungsten (W); Vanadium (V); Zinc (Zn); Zirconium (Zr)
Non-exhaustive list
- Formate; Acetate; Propionate; Acrylate; Lactate; Butyrate; Isobutyrate; Maleate; Valerate; Isovalerate; Caproate
Non-exhaustive list
Please contact us
Please contact us
Please contact us